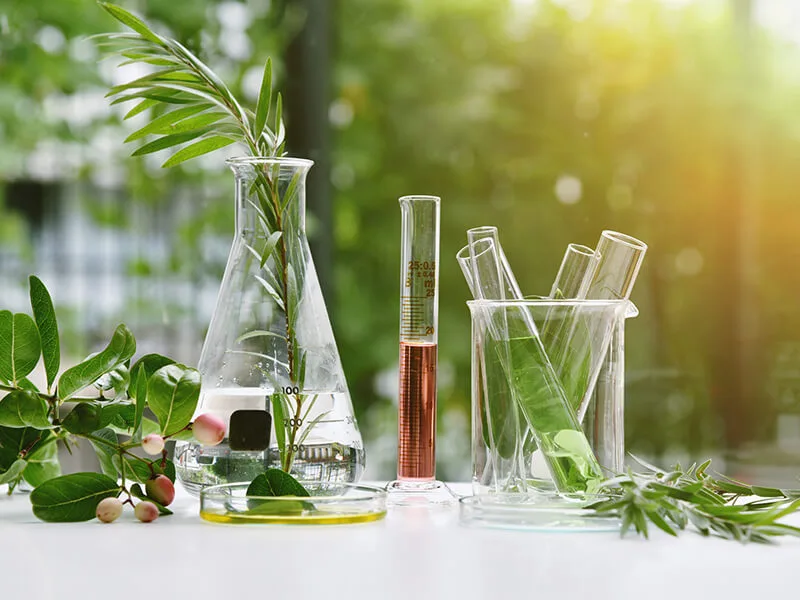
Naturopathy, a holistic approach to healthcare that emphasizes the body’s innate ability to heal itself, has gained popularity in recent years as individuals seek alternative and complementary therapies. While conventional medicine remains a cornerstone in treating many illnesses, some people turn to naturopaths in the hope of finding personalized, natural solutions. This article by Kelowna chiropractors explores the potential benefits and limitations of naturopathy in addressing various illnesses.
Naturopathy, a holistic approach to healthcare that emphasizes the body’s innate ability to heal itself, has gained popularity in recent years as individuals seek alternative and complementary therapies. While conventional medicine remains a cornerstone in treating many illnesses, some people turn to naturopaths in the hope of finding personalized, natural solutions. This article by Kelowna chiropractors explores the potential benefits and limitations of naturopathy in addressing various illnesses.
Principles of Naturopathy:
Naturopathy is guided by several principles, including the belief in the healing power of nature, identifying and treating the root cause of illness, and promoting prevention. Naturopaths often employ a combination of dietary changes, herbal remedies, lifestyle modifications, and other natural therapies to support the body’s self-healing mechanisms.
Key Modalities in Naturopathy:
- Nutrition: Naturopaths emphasize the importance of a well-balanced diet to support overall health and treat specific conditions. They may recommend dietary changes, supplements, or herbal remedies to address nutritional deficiencies or imbalances.
- Herbal Medicine: The use of plant-based remedies is a cornerstone of naturopathy. Naturopaths may prescribe herbal supplements or teas to alleviate symptoms and support the body’s healing processes.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Naturopaths often work with individuals to identify and address lifestyle factors contributing to illness. This may include stress management, exercise, and adequate sleep to enhance overall well-being.
- Detoxification: Naturopathy places importance on supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes. Therapies such as fasting, hydrotherapy, or specific diets may be recommended to eliminate toxins and promote healing.
Potential Benefits of Naturopathy:
- Personalized Approach: Naturopaths often take a holistic and individualized approach, considering the unique circumstances of each patient. This personalized care may lead to more tailored and patient-specific interventions.
- Preventive Focus: Naturopathy places a strong emphasis on preventive healthcare. By addressing lifestyle factors and promoting healthy habits, naturopaths aim to prevent the onset or recurrence of illnesses.
- Integration with Conventional Medicine: In some cases, naturopathy can be integrated with conventional medical treatments, providing a complementary approach to address both the symptoms and underlying causes of illness.
Limitations and Considerations:
- Scientific Evidence: While some natural therapies have demonstrated efficacy, the scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of certain naturopathic interventions can be limited. It’s essential to critically evaluate the evidence for specific treatments.
- Not a Replacement for Conventional Medicine: Naturopathy should not be viewed as a substitute for conventional medical care, especially in the case of serious or acute illnesses. It is crucial to consult with medical professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Varying Regulations: The practice of naturopathy is subject to varying regulations worldwide, and the qualifications of practitioners may differ. It’s advisable to seek care from licensed and reputable naturopaths.
Naturopathy offers a holistic and personalized approach to healthcare, focusing on the body’s ability to heal itself. While it may provide benefits in supporting overall well-being and managing certain conditions, it is essential for individuals to make informed decisions, considering both the strengths and limitations of naturopathic interventions. Integrating naturopathy with conventional medicine, under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals, may offer a comprehensive and balanced approach to managing illness. As with any healthcare decision, individuals should consult with both naturopaths and conventional medical practitioners to ensure the best possible care for their specific health needs.